 Linksys Help Page
Linksys Help Page
http://www.hansenonline.net/Networking/LinksysNews.html
DSL Reports LinkSys Help/Problems Forum
http://www.dslreports.com/forum/equip,16
Open your Web Browser. IE or Netscape is fine.
1) Type the IP for your Linksys Box. By default that is 192.168.1.1
2) A Username / Password Window will appear. You only need a
Password. By default Linky's ship with admin
all lower case.
type in your password and press enter.

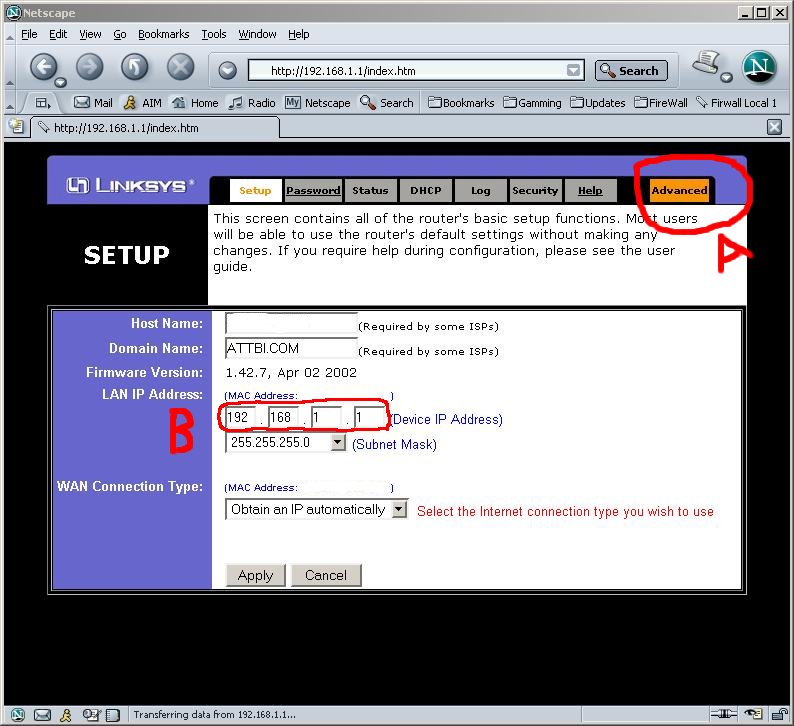
When you first log into your router this is the first page you will see.
Figure B This shows what
your Current Linky's IP is. If you were to ping this IP the Router itself
would answer.
This is also the IP you need when setting up a Static IP, because this become
your Gateway IP.
Host Name: This is a ID or
Name that is provided by your ISP service. This is also the Computer
Name
that your ISP service has given you. This can be used in conjunction with
MACK cloning to help in using your router.
Domain Name: This is a ID or Name that is provided by your ISP service. This can be used in conjunction with MACK cloning to help in using your router.
Firmware Version: This is the current Version of the Firmware you are using.
Wan Connection Type: This is tells the router to either get the IP info automatically or it can be set with permanent info provided by your ISP.
When you first log into your router this is the first page you will see.
Figure A. This is the tab
or link you use to get your advanced options. This includes
Port Forwarding, DMZ, and Filters.
Figure B. This shows what
your Current Linky's IP is. If you were to ping this IP the Router itself
would answer.
This is also the IP you need when setting up a Static IP, because this become
your Gateway IP.

Before starting forwarding ports, I'd like to take a minute to go over what is needed to use static IP addresses on your LAN. With DHCP all the IP configuration information is passed on to all the clients. This includes IP address, default gateway IP address and the IP addresses of up to three DNS servers. Even if you disable DNS in TCP/IP properties, the DHCP server will still give you the DNS server to allow the computer to resolve names.
When using static IP addresses, you have to provide all this information yourself. And, you have to enable DNS. This is the only way you can enter DNS server information, and without it, you will not be having any fun.
So, if you are going to use static IP addresses, you'll need to enter at least one DNS server address and a default gateway address, plus a static IP address that is outside the range of what the router hands out. By default, the range used by the Linksys router is 192.168.1.100 through 192.168.1.150. Stay clear of those address (you have 203 other to choose from!). Another idea is to keep the Static IP LOWER than 100 or what you have set in the Starting IP Address field.
The documentation that comes with the router claims that you must disable the DHCP server if you are going to use port forwarding; also, the configuration page where you set up the port forwarding says the same thing. This is INCORRECT! You do not have to disable the DHCP server on the Linksys router to use any of the features on the router 1). What Linksys probably should have said is that it makes sense to use static IP addresses on the machines you are forwarding ports to (disable DHCP on the client).
Now that you have all you Network settings from your STATUS page you should go ahead and input all that info into windows network configuration. Once that is done then reboot the computer.
IMPORTANT
If you DNS, or Gateway IP change the computer that you set a static IP on will
not have this new info. In this case your Static Computer will not work until
you enter the new changed information.
See Also
How to find your computers IP Address...
DHCP what is it?...
List of well known ports...
Game Server Ports...
Port forwarding is a way of allowing outside users access to your LAN computers on a given port (or range of ports). Basically, if someone connects to the WAN IP address on port 80 on your router and you have set port 80 to be forwarded to an IP address on your LAN, then the router will allow that traffic to pass right through to the destination. To the outside world, it will seem like they are accessing the web server directly on the WAN IP address. The same goes for other services.
This is directly linked to the use of static IP address. The documentation that comes with the router claims that you must disable the DHCP server if you are going to use port forwarding; also, the config page where you set up the port forwarding says the same thing. This is INCORRECT! You do not have to disable the DHCP server on the Linksys router to use any of the features on the router 1). What Linksys probably should have said is that it makes sense to use static IP addresses on the machines you are forwarding ports to (disable DHCP on the client). When using DHCP, it is possible that you will not get the same IP address you had the last time. If you are forwarding ports to the old IP address, outside users will not be able to connect as the router will direct the traffic to the wrong computer. So, if you are going to set up a web server or a mail server, or any other type of server, then use a static IP address on that computer.
With firmware 1.37, you can also specify TCP, UPD or Both to have better control over what type of traffic should be passed on to your LAN.
With Firmware 1.4+, you can also set up standard Port forwarding for HTTP, FTP, Telnet and others under the new "UPnP Forwarding" button found at the bottom of the "Forwarding" page.
How to Setup Port Forwarding.
Forwarding ports is actually quite simple. Using a web browser, connect to
the LAN IP(192.168.1.1 default) of the router, and click the orange "Advanced" tab in the
top-right corner. Then click the "Forwarding" tab to get to the port
forwarding configuration screen. You can forward up to 10 ranges of ports.
Simply enter the start port and the end port (same number in both if there's
only one port), then enter the IP address of the computer you wish to forward
to. If your the only computer on the router then you can use
192.168.1.100, and then click the Apply button to save configuration. Once the
router has re-started, traffic will be forwarded to the IP address selected.
Also Please remember Port Forwarding will not work if SPI is turned on.
See Also
Setting a Static/Permanent IP address on your PC...
How to find your computers IP Address...
DHCP what is it?...
List of well known ports...
Game Server Ports...
Port Triggering...
| DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP for short, is a convenient way for computers on a network to identify each other and make sure that data is transferred correctly. In order to better understand this, it is necessary to explain Internet Protocol (IP), and, more specifically, IP Addressing. Using the Internet Protocol, computers and other networking devices on a network are assigned an identifying number, referred to as an IP Address. This address can be compared to the address of your house, and the mail that is delivered to you is like data. The postal worker knows to deliver mail (data) to your house by your address. The same is true for computers on a network. The network knows where to deliver data, according to the IP address it is being sent to. An IP address is in the form of XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX and must be unique for every computer on the network - if two houses in the same town had the same address, the mail (data) would always be mixed up! IP addresses can be assigned in one of two ways. Using Static IP Addressing, each computer on a network is assigned a static, or permanent, IP address, just as your house has a permanent address. This address is usually assigned by a person, such as a network administrator. In the case of large networks (like the Internet), this can be very time consuming. The list of IP addresses in a large network and how they have been assigned can make record-keeping a full time job. However, it is still an effective and even easy way to assign IP addresses in a smaller network. In larger networks, however, another way to assign IP addresses was needed. After all, in large companies, employees and computers are often moved on the network. Employees often have to log onto the network from remote locations, like hotel rooms when business traveling. If you physically moved your house to another part of town every week, imagine how difficult it would be for people to keep up with your address! (And how much the post office would resent you!) This is where DHCP comes in. This protocol actually leases, or temporarily assigns, an available IP address to computers as they log on to the network. This IP address belongs to that computer during that session. When that computer is logged off the network, DHCP can assign that IP address to another computer when it logs on. The network keeps up with you efficiently, with no wasted IP address space. Other users (and network administrators) don't have to keep up with your address. And, in some ways, this provides some measure of safety from hackers, since you are not at the same IP address all the time. DHCP is built into some operating systems, like Windows NT and Windows 2000. For users of operating systems like Windows 98 or Millennium, however, DHCP must be administered through another method. |
|
See Also
Setting a Static/Permanent IP address on your PC...
How to find your computers IP Address...
I briefly touched on filters in the Basics page. Think of filters as the opposite of forwarding. It only works from the inside (as opposed to forwarding which works only on the outside), and instead of allowing traffic, it blocks it. This is one way to prevent certain types of traffic to leave your network. In the Basics page I set up a filter to block NetBIOS traffic from going out. If you have any application that are strictly LAN based, and you want to make 100% sure that it does not transmit any data onto the Internet, then you can filter out the port (or range of ports) on. As with Forwarding, this is in the Advanced section.
I am filtering ports 135 - 139 and also port 1975. There was a big controversy a short time ago about Aureate/Radiate and their software. Some "freeware" (or adware, really) applications comes with advertising built in. In stead of you paying for the program, you get to watch some ads as you use the software. The software also keeps track of which web sites you go to so it can better determine what types of ads it should display on your computer. The Aureate/Radiate spyware application uses (or used) port 1975 to talk to mother. Although I don't have any of the spyware, I'm still blocking that port.
For a home network, leave these at the defaults. This only applies if you have multiple routers on your network, and most home networks would not need this.
This is a fairly new feature. Logging can be disabled or enabled. If enabled and with "255" left as the last byte of the IP address, the router will broadcast log information onto your LAN, hoping that some program will catch the information. If you want to capture this information, you're better of specifying the IP address where the logging application is running (see Setting a Static/Permanent IP address on your PC... above). You can also view the access logs on the router, but there's hardly any information there. It lists the IP address and port number of traffic passing through the router. This is fine to check and see if your SMTP traffic gets through, but it doesn't tell you anything about what else is hitting your router. You have no way of knowing if someone is trying to access a Sub-7 trojan on your computer, or is someone is doing a port-scan to see what ports are open.
Since I'm running a web-server, the access log would be redundant, so I disabled it. The program "LogViewer" is available from LinkSys. The better bet is to use the WallWatcher tool click HERE to check it out.
See Also
Setting a Static/Permanent IP address on your PC...
Utilities For the Linksys...
How to find your computers IP Address...
DHCP what is it?...
Linksys have chosen an interesting definition of DMZ(Demilitarized Zone). Essentially, it's a "public" computer. Setting the IP address in the DMZ field to match that of a computer on your LAN, you are essentially placing that computer outside the router. That means the computer is not protected by the router. Any incoming traffic which is not forwarded somewhere else will be forwarded to the computer in the DMZ. This is not a good place to be, but unfortunately, sometimes it is required. If you wish to use MS NetMeeting, you need to place your computer in the DMZ. Due to the fact that MS NetMeeting uses some random port allocation, the router wouldn't be able to pass the traffic to your computer otherwise.
How to set the DMZ
Open your Web browser and enter the 192.168.1.1. When prompted enter you
password(Default is Admin). Select the Orange "Advance"
Tab, then Click the "DMZ Host" Tab and enter the last 3 digits of your
IP address(100 is correct if your the only computer on you router). Then
Press "Apply" Button to save the changes.
See Also
Port Forwarding...
Setting a Static/Permanent IP address on your PC...
How to find your computers IP Address...
DHCP what is it?...
IP Poster - This tool can auto-update a web page
with the LinkSys's WAN IP.
Click HERE to
DownLoad.
Click HERE for Installing and using IP Poster.
WallWatcher - Advanced Firewall Log program that
can log much more info then the normal Linksys LogViewer.
Click HERE to DownLoad.
MTU Size
This sets the maximum packet size that can be sent over the router. The maximum value is 1492. A smaller MTU forces more packets to be sent. More packets means more acknowledgement messages, and more packet header information. So, setting a smaller MTU value basically increases network overhead. However, if you have a network with high packet losses, it might be better to have a lower MTU size. (Resending a lost smaller packet is not so bad as having to resend a larger one.)
You'll want to make sure that your host has the same MTU size, or smaller. If you try to send a packet with a larger MTU size than the router supports, the router should respond with a ICMP 'Fragmentation required - DF set' message.1 This is bad, more network overhead, and your host is going to have to split up the packet anyway. A program that will let you tweak your PC network settings, such as MTU size is called DrTCP and can be found at DSLReports.com.
This router setting inforces the outgoing connection's MTU. Incoming (server) connections are not affected by this setting.
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI)
Basically this is a Good Thing™. However, according to our friends at the BEFSR41 news site , you cannot use SPI with port forwarding. Port triggering, however, still seems to work with SPI enabled! Hopefully port forwarding will too in future firmware revisions. Basically, if you set up the router for any servers you can't use SPI.
SPI looks at each packet a little more in depth than just normal routing.3 It checks where the packet is going and where it is from and remembers this info for the future. If a packet comes to your door that has the right routing information, a normal NAT might just pass the packet on regardless. However, an SPI firewall might say, 'Hey, wait a minute, this packet is from somewhere that I haven't visited lately, its unsolicited, so I'm just going to ignore it.'
This has the effect of blocking unwanted bad stuff like trojan connection attempts and port scans. If a packet arrives that doesn't match one of your outgoing connections, it is simply ignored.
Port Triggering Overview
This is pretty slick (in my opinion). Basically, its standard port forwarding with a twist. When the router detects an outgoing connection on a specific port range, it will set up an incoming port forwarding rule (temporarily) on the ports you specify.
The BEFSR41 news site mentioned earlier has a good example of this involving SMTP. Another example is IRC. When you connect to an IRC server, often the IRC server connects back on 113 for an Ident lookup. However, often your router blocks these requests from getting back to your PC. If you were to set up a port trigger on ports 6000-7000 (a wide swath of ports, yes, but IRC servers usually are within this range) to forward the incoming port range 113-113, then the router will pass Ident requests.
Port Triggering - What is it?
or...
Everything You Always Wanted to Know About Port Triggering But Were Afraid To Ask...
I have some applications for the newest BEFSR41 Port Triggering function so decided to test what it can and cannot do. I was a little disappointed it wasn't more elaborate but I guess I was expecting more.
All this info was compiled on a BEFSR41 f/w version 1.39.
What Is Port Triggering?
I think of Port Triggering as a way to dynamically forward ports to a LAN PC that needs them at a particular time. That particular time is when it runs a certain application that performs some event that "triggers" the router. This event must be an outbound access of a particular port range.
What is an example of Port Triggering use?
Connecting to an IRC server that needs an IDENT reply from you.
When you connect to an IRC server you use a port in the range 6660-6670. This connection is an ideal trigger because shortly after connecting the server will try and connect to your IDENT server to get a reply. Your end has to become an IDENT server and popular IRC client programs like mIRC have this server built in. But to make that PC an IDENT server it needs IDENT (port 113) forwarded to it.
I have 3 PCs getting LAN addresses automatically via DHCP so I cannot forward to them, right?"
The beauty of Port Triggering is it's dynamic like DHCP is. "Regular" Port Forwarding is static and should be to a static IP but Port Triggering is not static - it will work with DHCP LAN PC addresses!
Unfortunately, IRC's DCC (Direct-Client-to-Client) file transfer and chat functions needs other forwarded ports so just the IDENT example won't work by itself if you want to use DCC.
How would I set up Port Triggering for mIRC?
Go to the Advanced->Forwarding tab to find the "Port Triggering" button. Fill in this info on line 1:
Application Name: mIRC-IDENT
Trigger Port Range: 6660 - 6670
Incoming Port Range: 113 - 113
Press "Apply" then close the box with the "X". I found version 1.39 to be a bit strange when I hit "Cancel" or "Apply" more than once - I had to reset the router sometimes.
Can't the LinkSys know when mIRC is being run?
Absolutely not. Well, not like a personal firewall can. The LinkSys router is independant of the LAN PC's programs and operating system.
Then what's the "Application Name" do?
It's a reference so you know what the entry is for - what you put in does not affect the function.
So I can run any LAN PC on IRC and it will get IDENT forwarded to it?
Yes, you should be able to BUT... watch out for...
And run 2 PCs at the same time?
I knew you'd ask that! IRC is not a good example because if you try this on 2 PCs at the same time I find ONE AND ONLY ONE PC will get forwarded. This was part of my disappointment.
That's no good! I want to run 2 PCs at the same time on IRC!
What will happen on IRC is if PC#1 connects to an IRC server it will get IDENT fine. If PC#2 shortly comes along and connects to an IRC server PC#1 will still be forwarded IDENT. What's funny about this is PC#2 may connect just fine but it's PC#1's IDENT reply that did it! Fun, huh?
Be careful, this may not always happen because mIRC has an IDENT option "Enable only when connecting" so PC#1, even though it has IDENT forwarded to it may already be connected and not IDENT reply for PC#2.
IRC IDENT is a poor example for wanting to run 2 PCs at the same time using Port Triggering. Many games can make use of Port Triggering but the game would get all screwed up if the right PC didn't get the ports forwarded.
So what good is Port Triggering?
Well, you can't exactly run 2 PCs on Port Triggering at the same time but at least you don't have to change Port Forwarding for each PC when it wants to run IRC or a game that needs Port Triggering.
So when my sister gets done when can I get on with my PC?
You may have to wait up to 2 minutes is what I measured. My testing goes like this:
Once "triggered" the forwarding happens for 2 minutes unless a forwarded packet comes in OR another trigger event happens. Either resets this 2 minute timer. Once the 2 minute timer times out the next PC that triggers the magic event will "take over" the Port Triggering function.
What if my sister and I are on different IRC servers? Will it work then?
No, this is another disappointment my testing showed. I was hoping if different servers were used only the server triggered would be individually forwarded to the individual PC that caused it. But this is not the case.
Is the forwarding produced by Port Triggering only from the triggering server?
No, my testing showed it is a *global* forward. When Port Triggering is forwarding to a PC that PC is fully open on those "Incoming" ports from any host on the internet - the same as *regular* Port Forwarding.
On version 1.39 Port Forwarding doesn't work if SPI is enabled. Same with Port Triggering?
No! Port Triggering works even when SPI is turned on in version 1.39 (and 1.38.5 I suspect, too, but I only tested 1.39).
I want to run some games that connects to a game server but it doesn't work unless I forward certain ports. Will Port Triggering allow me to run that game from any PC?
Possibly. Check support boards for each game or check the "Web Links" ports list above to identify a "Trigger Port Range" which is usually the port(s) you connect to the server with. Then set the "Incoming Port Range" the same as the forwarded ports you needed before.
Keep in mind only one LAN PC can run the same game at any one time.
Can 2 different games be played?
I didn't test this but I do know one thing... if "Trigger Port Range" or "Incoming Port Range" overlaps between the 2 games it would be a fight to see which game works!
Can I run a game server using Port Triggering?
I doubt it. Port Triggering is initiated from a LAN PC, NOT users out on the internet. Port Triggering has very limited value for servers - use Port Forwarding.
Hidden Features in the 1.39.2+ Firmware
IMPORTANT! For reasons we can probably guess, these features have been intentionally hidden by the firmware coders. It stands to reason that they don't work, or that they're extremely buggy. I do not advocate trying these hidden features. If you opt to play with these features, you do so AT YOUR OWN RISK.
I'm going to assume you're router is at 192.168.1.1 and has the default password of 'admin'. If it does not, you'll need to modify these links to get them to point to your router. Also, I've intentionally not made them real links because you really shouldn't be trying this at home.
Enhanced Logging Functions (aka Diagnostic Logging)
There are some hidden logging functions available in this firmware. This log information is sent to a client PC in the same way that the traffic logs are, via SNMPTrap. According to "mole2" this used to be known as "diagnostic logging" in previous firmware versions.11
http://admin:admin@192.168.1.1/LogManage.htm
The extending logging exists in the BEFSR41 as well. You can easily access this feature by clicking the "Log" tab, then click around the top of the "Log" tab near the blue bar. I couldn't find it at first because the mouse cursor didn't change into the "finger" pointer for some reason.
As far as I can tell, you can check off which SNMP messages you'd like your router to send out. However, most logging clients for the BEFW11S4 don't really know about these new logging functions.
SNMP Trap Watcher can receive all of the SNMP Messages that the router sends, apparently. I also recommend WallWatcher. Check out Utilities For the Linksys... for the WallWatcher.
See Also
Setting a Static/Permanent IP address on your PC...
Utilities For the Linksys...
How to find your computers IP Address...
Internal IP(Local LAN IP)
For Win98 or WinMe
To Find your IP Address go to start, run and then type in 'WINIPCFG' and press 'OK'
Change from PPP and select your LAN Nic Card. This will then show you your internal IP. This value should be typed into the IP Address field on the LinkSys Router.
Internal IP(Local LAN IP)
For Win2k or WinXP
Go to START, RUN and type in 'Command' and press 'OK'
Then in the DOS box type in "ipconfig /all"
Under the Heading of 'IP Address.....' will be listed your internal IP. This value should be typed into the IP Address field on the LinkSys Router.
External IP(internet IP or WAN IP)
Open up your browser to 192.168.1.1 type in your password
Click on the 'Status' Tab.
Under WAN: you will find your External, Internet, WAN IP address.
The following tips may help you with the firmware upgrade process:
Try the new TFTP2 upgrade utility. Download from here.
It's a good idea to download a copy of the existing version of your firmware from the Linksys FTP site, so that you can restore it in case something goes wrong with the newer version of firmware that you are trying to load. If you can't find your exact version, just download the latest released version.
Does the upgrade program successfully finish, but you can't bring up the Admin page?
Try backing off to the previous version of firmware and use the "Advance" button on the Upgrade Firmware program and set it to send Filename with path, and change the Initial delay to 1000ms.
The TFTP upgrade server is burned into the ROM of the router, and can't be erased. If something goes wrong with the upgrade and you get the dreaded steady "Diag" light on the router, just repeat the upgrade.
If you are having a NIC connection problem, you may have an upgrade fail and not be able to resurrect the router. DON'T PANIC!!!
Either connect the router to another computer with a different NIC, or connect a hub between your computer and the router (don't connect "Uplink" to "Uplink", connect "Uplink to a NORMAL port), and retry the upgrade.
You might have a problem upgrading or logging into the router if you use too strong a password. Some versions of the firmware are reported to have problems with mixed upper & lower case letters, or with characters other than numbers and letters. Some users have been able to use their password successfully on the router, but have it fail when trying to use the TFTP upgrade client.
We recommend trying to use as strong a password as possible, but if you have problems, try using a simpler password. You should also stay away from the characters "/" and "\" in your passwords, keep the length under 39 characters, and do not use any spaces in the password (your browser will translate the space character to '+').
Some firmware versions reset the password to "admin", so try that if your normal password doesn't work.
If you still have problems upgrading due to getting your password rejected, try entering a blank password, then try the upgrade. Be sure to restore your password after you've successfully upgraded!
STILL can't get the firmware to load? See this tip.
Here's a copy of the installation instructions (Readme.doc) file that comes with the upgrade file:
How to upgrade the BEFSR41 Firmware
The firmware on the EtherFast Cable/DSL Router (BEFSR41) has a 512KB flash
chip that can be upgraded with a new firmware. Please read the instructions below to upgrade the firmware.
1. Double click on Tftp to install the Upgrade Firmware software. Follow the screen and accept the default settings by clicking on Next a few times, then click on finish to finish the installation.
2. Click on Start, Programs, Upgrade Firmware, then click on Upgrade Firmware. You should see the screen below.
3. The following option is available.
Server- Enter the IP Address of the BEFSR41 that you assigned. By default, the router is 192.168.1.1 as shown above.
Password- Enter the password you assigned the router. By default, the router’s password is “ADMIN”.
File- Click the triple “…” button to browse for the code.bin that was part of the extracted file you downloaded. In the example, the code.bin was extracted on the Windows desktop.
4. Click Upgrade button to start upgrading. A progress bar should show up to show the progress.
Upgrade is complete.
See Also
HELP- My router Diag light is blinking, how do I fix this?...
HELP- Reviving a "DEAD" Linky?...
HELP- My firmware has become
Sticky...
HELP- Need More Help...
UPnP NAT Traversal FAQ
Do you have questions about Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) and Network Address Translation (NAT)? This article provides answers to some of the most commonly asked questions about a variety of UPnP, NAT, and UPnP NAT Traversal issues.
Q. What is UPnP?
A. Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is an architecture for pervasive peer-to-peer network connectivity of PCs and intelligent devices or appliances, particularly within the home. UPnP builds on Internet standards and technologies, such as TCP/IP, HTTP, and XML, to enable these devices to automatically connect with one another and work together to make networking—particularly home networking—possible for more people.
Q. What does UPnP mean to the consumer?
A. Simplicity, choice and more innovative experiences. Networking products that include Universal Plug and Play technology will "just work" when physically connected to the network. UPnP can work with essentially any networking media technology, wired or wireless. This includes, for example: Category 5 Ethernet cable, Wi-Fi or 802.11B wireless networks, IEEE 1394 ("Firewire"), phoneline networking or powerline networking. As these devices and PCs are connected with one another, it becomes easier for users to take advantage of innovative new services and applications.
Q. What is the UPnP Forum?
A. The Universal Plug and Play Forum is an open industry consortium that was formed in June 1999 to help define the UPnP standards to simplify the networking of intelligent devices in homes and, longer term, within enterprises. The forum is achieving this goal by defining and publishing UPnP device control protocols and service control protocols. As of early June 2001, more than 350 companies are members of the UPnP Forum. The UPnP Forum is directed by the 22-member UPnP Steering Committee. A Technical Committee, Marketing Committee and a variety of working committees, each focused on a specific device category, also are set up to carry out the organization's efforts. A list of forum members, along with information on joining, is available at the forum Web site.
Q. What are the technical elements of UPnP?
A. UPnP is broad in scope in that it targets home networks, proximity networks, and networks in small businesses and commercial buildings. It enables data communication between any two devices under the command of any control device on the network. UPnP is independent of any particular operating system, programming language, or physical medium. UPnP supports zero-configuration networking and automatic discovery, whereby a device can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP address, announce its name, convey its capabilities upon request, and learn about the presence and capabilities of other devices. DHCP and DNS servers are optional and will be used if available on the network. Furthermore, a device can leave a network smoothly and automatically without leaving any unwanted state behind. UPnP learns from the Internet's success and heavily leverages its components, including IP, TCP, UDP, HTTP, and XML. UPnP involves a multi-vendor collaboration for establishing standard Device Control Protocols (DCPs). Similar to the Internet, these are contracts based on wire protocols that are declarative, expressed in XML, and communicated via HTTP.
Q. What is NAT? Why is it used?
A. Network Address Translation is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard used to allow multiple PCs or devices on a private network (using private address ranges such as 10.0.x.x, 192.168.x.x, 172.x.x.x) to share a single, globally routable IPv4 address. A main reason NAT is often deployed is because IPv4—the current generation of the Internet - addresses are getting scarce.
NAT is used in gateway devices that form the boundary between the public Internet and the private LAN. As IP packets from the private LAN traverse the gateway, NAT translates a private IP address and port number to a public IP address and port number, tracking those translations to keep individual sessions intact. Internet Connection Sharing in Microsoft® Windows® XP and Windows Me operating systems, along with many Internet gateway devices use NAT, particularly to connect to broadband networks such via DSL or cable modems. The use of NAT is increasing dramatically as more homes and small businesses network their PCs and share a connection to the Internet.
Q. What is the problem with NAT?
A. Put simply: NAT can "break" many of the compelling new PC and home networking experiences, such as multi-player games, real time communications, and other peer-to-peer services, that people increasingly want to use in their homes or small businesses. These applications will break if they use private address on the public Internet or simultaneous use of the same port number. Application must use a public address and for each session a unique port number. Large organizations have professional IT staff on hand to ensure their corporate applications can work with NAT, but smaller organizations and consumers do not have this luxury. UPnP NAT Traversal can automatically solve many of the problems the NAT imposes on applications, making this an ideal solution for small businesses and consumers.
Q. Who came up with the NAT traversal solution?
A. The NAT traversal solution is part of the work being done on the specification for the Internet Gateway Device (IGD) by the UPnP IGD Working Committee. UPnP member companies may join this committee or merely choose to monitor its progress. The chair of the committee is Prakash Iyer from Intel (prakash.iyer@intel.com). Many organizations, including Microsoft, drove this effort.
Q. Are there other ways to solve the problem of NAT traversal? If so, why is using UPnP the best choice?
A. Yes, there are other ways to solve this problem, but no other mechanism currently exists as an industry standard to address this problem in an automatic way for the consumer and in such a universally-applicable way for the developer. Other approaches require either manual intervention by the user or they require special development efforts by the Internet gateway device vendor and the software developer to handle the NAT traversal needs of specific applications. As a result, UPnP is uniquely able to solve this important problem.
Consumer does the work. The manual intervention methods of NAT traversal require a consumer to use a browser, a graphical user interface-based tool on the PC, or a command line interface tool on the PC to change some settings on the Internet gateway device in the home. While some technical enthusiast users have little difficulty with this, many consumers do not feel comfortable doing this. Further, many consumers may not even realize that NAT traversal problems are interfering with their use of services across the Internet. The user may be attempting to play a multi-player game or engage in some other peer-to-peer service but find he or she cannot connect for some reason. This leads to troubleshooting, support calls, customer dissatisfaction, and reluctance on the part of the user to try new services or experiences in the future.
Developer does the work. To avoid requiring the consumer to solve this NAT traversal problem manually, some Internet gateway device vendors have written and included application layer gateway support into their devices. This application layer gateway software is designed with specific applications in mind. In other words, the device vendor writes and tests specific code that will automatically enable one application to go through the NAT. If the application software is updated, the application layer code the device vendor wrote may have to be updated and tested again. This one-at-a-time way of chasing the NAT traversal problem is manageable for device vendors when there are only a few peer-to-peer or relevant applications to consider, but this approach does not scale well to 100s or 1000s of applications, can be very expensive to pursue, and likely requires specific knowledge of how each of these applications function. The better way to approach this problem is to have the device vendor add software or firmware to their device once to understand UPnP and have other devices and software be able to communicate with the NAT device using this same technology. UPnP is uniquely able to fulfill this role today.
Q. What does the UPnP NAT traversal solution do?
A. The scenarios that UPnP-enabled NAT traversal helps ensure include:
Multi-player gaming
Peer-to-peer connections
Real time communications
Remote Assistance (a feature in Windows XP)
For IHVs this solution removes the need for writing and maintaining a database of Application Layer Gateways (ALGs) to traverse the NAT. This solution will be supported by both Windows XP and Direct Play, a programming resource in Windows, so software applications written to DPlay will be able to use the UPnP solution for NAT traversal automatically.
The UPnP Forum's IGD spec achieves this automatic NAT traversal by providing methods for the following:
Learning public IP address
Enumerating existing port mappings
Adding and removing port mappings
Assigning lease times to mappings
Q. Which vendors are implementing the UPnP NAT traversal solution?
A. Currently most of the large gateway (DSL/Cable router) vendors have announced intentions to implement the UPnP NAT traversal solution in products they ship in 2001, beginning as soon as July. They include: Microsoft in WindowsXP, Linksys, D-Link, Intel, Netgear and Buffalo Technology, and Arescom. Some of these vendors have announced they will provide firmware or software upgrades to customers who already own their devices to add support for UPnP-enabled NAT traversal.
Q. How does a consumer know which Internet gateway device has UPnP support?
A. Consumers can check the Web site of their Internet gateway device vendor or read the label on the product packaging to see if this feature is included. Some retailers will know about this within the next few months. In the coming months, the UPnP Forum will make available a UPnP logo that vendors can include in their product packaging, marketing materials or on the products to indicate the product meets UPnP Forum's test requirements.
Q. What resources are available to developers to implement this?
A. There are a number of resources, from whitepapers to interoperability testing events (PlugFests). For technical papers, please go to http://www.upnp.org/resources.htm. For upcoming events, please see http://www.upnp.org/events.htm. Microsoft provides developer information for Windows XP on MSDN Online.
P R O B L E M
My router Diag light is blinking after a Firmware Upgrade, how do I fix this?
S O L U T I O N
This is caused by a firmware not loading correctly. Follow the steps below to fix this.
Download the latest release firmware for your router from http://www.linksys.com/download/firmware.asp. Be sure to select the correct model number of your unit.
Once downloaded, extract the files to a folder where you will be able to locate them.
The following files will be needed to perform the firmware upgrade:
TFTP.exe
Code.Bin
Before performing the upgrade, it is recommended to do the following:
assign your computer a static IP address, for more information on this, see Setting a Static/Permanent IP address on your PC...
if using a 10/100 network adapter, change the speed to 10Mb ½ duplex.
At the windows desktop, go to:
Start > Settings > Control Panel
Double click on the network icon.
This will bring up the Network Configuration window.
Once in the Network Configuration, highlight the icon with the green logo for your network adapter, and click on the word Properties
This will bring up the Properties for the network adapter.
Go to the Advanced tab, select Connection Type
* Note - The wording will vary depending on the make and model of your network adapter. Media Type, Connection Speed are two other wordings for the same function.
Change the value to the 10Base-t ½ duplex mode. This may also vary by make and model of the Network Adapter.
Once this is changed, click ok to go back to the Network configuration.
Click ok again and windows will ask to restart to make the changes.
Once this is done and the machine reboots, ½ duplex.
You are now ready to load the firmware on the router.
To test communication between the router and the network card do the following:
Go to Start > Run > type in: command and press enter.
This will bring up the MS-DOS prompt.
C:\WINDOWS\DESKTOP>
Type in: ping 192.168.1.1.
C:\WINDOWS\DESKTOP>ping 192.168.1.1
The following result should appear.
Pinging 192.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Now open the TFTP loader and there should be three fields in which to use:
Server
Password
File
the fields next to these should look as follows:
Server: 192.168.1.1
Password: ****** [this is admin by default, unless it has been changed]
File: C:\windows\desktop\code.bin [this would be how the file name would appear if you had saved the file to the desktop. For other folders, the path will look diffrerent]
Click on Upgrade.
A bar should appear in a box showing the status of the upgrade.
Once to the end the bar should disappear and a message that the firmware uploaded successfully should appear.
The light on the router should now have stopped blinking.
If this does not work, or you you are haiving difficulties in loading the firmware, contact Linksys technical support for further resolution.
See Also
HELP- Reviving a
"DEAD" Linky?...
HELP- My firmware has become Sticky...
HELP- Need More Help...
If you follow this procedure, you should be able to successfully load firmware into your router, even if you think you've tried everything. Follow the steps exactly and don't skip any!
To reload the firmware when an upload fails or when the red error light is blinking, do the following:
1) Set a static IP Address on the Windows PC as following:
IP Address: 192.168.1.50
Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.1
2) Make sure that you can execute the DOS command: "PING 192.168.1.1".
3) Make sure that the file name of the firmware code, given to TFTP.EXE, is "code.bin". RENAME the firmware file if you have to.
4) Try passwords in this order:
First: Try a blank password,
Second: Try "admin" (don't enter the quotes)
Third: The password you assigned previously
5) After successfully uploading the firmware, press the Reset button to clear memory and select default settings.
6) Reconfigure the LinkSys as required to support your Broadband environment.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Another reader suggested a simpler method for reviving Linky:
1) Press and hold the Reset button for about 30 seconds
Remove power. Wait about 5 seconds. Reapply power.
See Also
HELP- My router Diag light
is blinking, how do I fix this?...
HELP- My firmware has become Sticky...
HELP- Need More Help...
Sticky Firmware is any firmware version that will not flash up or down a version level.
To fix this please try the following method.
See Also
HELP- My router Diag light
is blinking, how do I fix this?...
HELP- Reviving a "DEAD" Linky?...
HELP- Need More Help...
DSL Reports LinkSys Help/Problems Forum
http://www.dslreports.com/forum/equip,16
See Also
HELP- My router Diag light
is blinking, how do I fix this?...
HELP- Reviving a "DEAD" Linky?...
HELP- My firmware has become Sticky...
1 tcpmux
2 compressnet
3 compressnet
5 rje
7 echo
9 discard
11 systat
13 daytime
17 qotd
18 msp
19 chargen
20 ftp-data
21 ftp
22 ssh
23 telnet
24 mail
25 smtp
27 nsw-fe
29 msg-icp
31 msg-auth
33 dsp
37 time
38 rap
39 rlp
41 graphics
42 nameserver
43 nicname
44 mpm-flags
45 mpm
46 mpm-snd
47 ni-ftp
48 auditd
49 tacacs
50 re-mail-ck
51 la-maint
52 xns-time
53 domain
54 xns-ch
55 isi-gl
56 xns-auth
58 xns-mail
61 ni-mail
62 acas
63 whois
64 covia
65 tacacs-ds
66 sql*net
67 bootps
68 bootpc
69 tftp
70 gopher
71 netrjs-1
72 netrjs-2
73 netrjs-3
74 netrjs-4
76 deos
78 vettcp
79 finger
80 http
81 hosts2-ns
82 xfer
83 mit-ml-dev
84 ctf
85 mit-ml-dev
86 mfcobol
88 kerberos
89 su-mit-tg
90 dnsix
91 mit-dov
92 npp
93 dcp
94 objcall
95 supdup
96 dixie
97 swift-rvf
98 tacnews
99 metagram
100 newacct
101 hostname
102 iso-tsap
103 gppitnp
104 acr-nema
105 cso
106 3com-tsmux
107 rtelnet
108 snagas
109 pop2
110 pop3
111 sunrpc
112 mcidas
113 auth
114 audionews
115 sftp
116 ansanotify
117 uucp-path
118 sqlserv
119 nntp
120 cfdptkt
121 erpc
122 smakynet
123 ntp
124 ansatrader
125 locus-map
126 unitary
127 locus-con
128 gss-xlicen
129 pwdgen
130 cisco-fna
131 cisco-tna
132 cisco-sys
133 statsrv
134 ingres-net
135 epmap
136 profile
137 netbios-ns
138 netbios-dgm
139 netbios-ssn
140 emfis-data
141 emfis-cntl
142 bl-idm
143 imap
144 news
145 uaac
146 iso-tp0
147 iso-ip
148 jargon
149 aed-512
150 sql-net
151 hems
152 bftp
153 sgmp
154 netsc-prod
155 netsc-dev
156 sqlsrv
157 knet-cmp
158 pcmail-srv
159 nss-routing
160 sgmp-traps
161 snmp
162 snmptrap
163 cmip-man
164 cmip-agent
165 xns-courier
166 s-net
167 namp
168 rsvd
169 send
170 print-srv
171 multiplex
172 cl/1
173 xyplex-mux
174 mailq
175 vmnet
176 genrad-mux
177 xdmcp
178 nextstep
179 bgp
180 ris
181 unify
182 audit
183 ocbinder
184 ocserver
185 remote-kis
186 kis
187 aci
188 mumps
189 qft
190 gacp
191 prospero
192 osu-nms
193 srmp
194 irc
195 dn6-nlm-aud
196 dn6-smm-red
197 dls
198 dls-mon
199 smux
200 src
201 at-rtmp
202 at-nbp
203 at-3
204 at-echo
205 at-5
206 at-zis
207 at-7
208 at-8
209 qmtp
210 z39.50
211 914c/g
212 anet
213 ipx
214 vmpwscs
215 softpc
216 CAIlic
217 dbase
218 mpp
219 uarps
220 imap3
221 fln-spx
222 rsh-spx
223 cdc
242 direct
243 sur-meas
244 dayna
245 link
246 dsp3270
256 rap
257 set
258 yak-chat
259 esro-gen
260 openport
261 naming-iiop-ssl
262 arcisdms
263 hdap
280 http-mgmt
281 personal-link
282 cableport-ax
309 entrusttime
344 pdap
345 pawserv
346 zserv
347 fatserv
348 csi-sgwp
349 mftp
350 matip-type-a
351 matip-type-b
371 clearcase
372 ulistproc
373 legent-1
374 legent-2
375 hassle
376 nip
377 tnETOS
378 dsETOS
379 is99c
380 is99s
381 hp-collector
382 hp-managed-node
383 hp-alarm-mgr
384 arns
385 ibm-app
386 asa
387 aurp
388 unidata-ldm
389 ldap
390 uis
391 synotics-relay
392 synotics-broker
393 dis
394 embl-ndt
395 netcp
396 netware-ip
397 mptn
398 kryptolan
399 iso-tsap-c2
400 work-sol
401 ups
402 genie
403 decap
404 nced
405 ncld
406 imsp
407 timbuktu
408 prm-sm
409 prm-nm
410 decladebug
411 rmt
412 synoptics-trap
413 smsp
414 infoseek
415 bnet
416 silverplatter
417 onmux
418 hyper-g
419 ariel1
420 smpte
421 ariel2
422 ariel3
423 opc-job-start
424 opc-job-track
425 icad-el
426 smartsdp
427 svrloc
428 ocs_cmu
429 ocs_amu
430 utmpsd
431 utmpcd
432 iasd
433 nnsp
434 mobileip-agent
435 mobilip-mn
436 dna-cml
437 comscm
438 dsfgw
439 dasp
440 sgcp
441 decvms-sysmgt
442 cvc_hostd
443 https
444 snpp
445 microsoft-ds
446 ddm-rdb
447 ddm-dfm
448 ddm-byte
449 as-servermap
450 tserver
451 sfs-smp-net
452 sfs-config
453 creativeserver
454 contentserver
455 creativepartnr
456 macon-tcp
457 scohelp
458 appleqtc
459 ampr-rcmd
460 skronk
461 datasurfsrv
462 datasurfsrvsec
463 alpes
464 kpasswd
465 ssmtp
466 digital-vrc
467 mylex-mapd
468 photuris
469 rcp
470 scx-proxy
471 mondex
472 ljk-login
473 hybrid-pop
474 tn-tl-w1
475 tcpnethaspsrv
476 tn-tl-fd1
477 ss7ns
478 spsc
479 iafserver
480 iafdbase
481 ph
482 bgs-nsi
483 ulpnet
484 integra-sme
485 powerburst
486 avian
487 saft
488 gss-http
489 nest-protocol
490 micom-pfs
491 go-login
492 ticf-1
493 ticf-2
494 pov-ray
495 intecourier
496 pim-rp-disc
497 dantz
498 siam
499 iso-ill
500 isakmp
501 stmf
502 asa-appl-proto
503 intrinsa
504 citadel
505 mailbox-lm
506 ohimsrv
507 crs
508 xvttp
509 snare
510 fcp
511 mynet
512 exec
513 login
514 shell
515 printer
516 videotex
517 talk
518 ntalk
519 utime
520 efs
521 ripng
522 ulp
523 ibm-db2
524 ncp
525 timed
526 tempo
527 stx
528 custix
529 irc-serv
530 courier
531 conference
532 netnews
533 netwall
534 mm-admin
535 iiop
536 opalis-rdv
537 nmsp
538 gdomap
539 apertus-ldp
540 uucp
541 uucp-rlogin
542 commerce
543 klogin
544 kshell
545 appleqtcsrvr
546 dhcpv6-client
547 dhcpv6-server
548 afpovertcp
549 idfp
550 new-rwho
551 cybercash
552 deviceshare
553 pirp
554 rtsp
555 dsf
556 remotefs
557 openvms-sysipc
558 sdnskmp
559 teedtap
560 rmonitor
561 monitor
562 chshell
563 snews
564 9pfs
565 whoami
566 streettalk
567 banyan-rpc
568 ms-shuttle
569 ms-rome
570 meter
571 meter
572 sonar
573 banyan-vip
574 ftp-agent
575 vemmi
576 ipcd
577 vnas
578 ipdd
579 decbsrv
580 sntp-heartbeat
581 bdp
600 ipcserver
606 urm
607 nqs
608 nsift-uft
609 npmp-trap
610 npmp-local
611 npmp-gui
612 hmmp-ind
613 hmmp-op
614 sshell
615 sco-inetmgr
616 sco-sysmgr
617 sco-dtmgr
618 dei-icda
619 digital-evm
620 sco-websrvrmgr
633 servstat
634 ginad
635 rlzdbase
636 ssl-ldap
637 lanserver
666 mdqs
667 disclose
668 mecomm
669 meregister
670 vacdsm-sws
671 vacdsm-app
672 vpps-qua
673 cimplex
674 acap
704 elcsd
705 agentx
709 entrust-kmsh
710 entrust-ash
729 netviewdm1
730 netviewdm2
731 netviewdm3
741 netgw
742 netrcs
744 flexlm
747 fujitsu-dev
748 ris-cm
749 kerberos-adm
750 rfile
751 pump
752 qrh
753 rrh
754 tell
758 nlogin
759 con
760 ns
761 rxe
762 quotad
763 cycleserv
764 omserv
765 webster
767 phonebook
769 vid
770 cadlock
771 rtip
772 cycleserv2
773 submit
774 rpasswd
775 entomb
776 wpages
780 wpgs
786 concert
800 mdbs_daemon
801 device
886 iclcnet-locate
887 iclcnet_svinfo
888 accessbuilder
911 xact-backup
991 nas
995 spop3
996 vsinet
997 maitrd
998 busboy
999 garcon
1000 cadlock
1025 blackjack
1027 ICQ
1030 iad1
1031 iad2
1032 iad3
1047 neod1
1048 neod2
1058 nim
1059 nimreg
1067 instl_boots
1068 instl_bootc
1080 socks
1083 ansoft-lm-1
1084 ansoft-lm-2
1110 nfsd-status
1123 murray
1155 nfa
1212 lupa
1222 nerv
1248 hermes
1313 bmc_patroldb
1314 pdps
1345 vpjp
1346 alta-ana-lm
1347 bbn-mmc
1348 bbn-mmx
1349 sbook
1350 editbench
1351 equationbuilder
1352 lotusnote
1353 relief
1354 rightbrain
1355 intuitive edge
1356 cuillamartin
1357 pegboard
1358 connlcli
1359 ftsrv
1360 mimer
1361 linx
1362 timeflies
1363 ndm-requester
1364 ndm-server
1365 adapt-sna
1366 netware-csp
1367 dcs
1368 screencast
1369 gv-us
1370 us-gv
1371 fc-cli
1372 fc-ser
1373 chromagrafx
1374 molly
1375 bytex
1376 ibm-pps
1377 cichlid
1378 elan
1379 dbreporter
1380 telesis-licman
1381 apple-licman
1382 udt_os
1383 gwha
1384 os-licman
1385 atex_elmd
1386 checksum
1387 cadsi-lm
1388 objective-dbc
1389 iclpv-dm
1390 iclpv-sc
1391 iclpv-sas
1392 iclpv-pm
1393 iclpv-nls
1394 iclpv-nlc
1395 iclpv-wsm
1396 dvl-activemail
1397 audio-activmail
1398 video-activmail
1399 cadkey-licman
1400 cadkey-tablet
1401 goldleaf-licman
1402 prm-sm-np
1403 prm-nm-np
1404 igi-lm
1405 ibm-res
1406 netlabs-lm
1407 dbsa-lm
1408 sophia-lm
1409 here-lm
1410 hiq
1411 af
1412 innosys
1413 innosys-acl
1414 ibm-mqseries
1415 dbstar
1416 novell-lu6.2
1417 timbuktu-srv1
1418 timbuktu-srv2
1419 timbuktu-srv3
1420 timbuktu-srv4
1421 gandalf-lm
1422 autodesk-lm
1423 essbase
1424 hybrid
1425 zion-lm
1426 sais
1427 mloadd
1428 informatik-lm
1429 nms
1430 tpdu
1431 rgtp
1432 blueberry-lm
1433 ms-sql-s
1434 ms-sql-m
1435 ibm-cics
1436 saism
1437 tabula
1438 eicon-server
1439 eicon-x25
1440 eicon-slp
1441 cadis-1
1442 cadis-2
1443 ies-lm
1444 marcam-lm
1445 proxima-lm
1446 ora-lm
1447 apri-lm
1448 oc-lm
1449 peport
1450 dwf
1451 infoman
1452 gtegsc-lm
1453 genie-lm
1454 interhdl_elmd
1455 esl-lm
1456 dca
1457 valisys-lm
1458 nrcabq-lm
1459 proshare1
1460 proshare2
1461 ibm_wrless_lan
1462 world-lm
1463 nucleus
1464 msl_lmd
1465 pipes
1466 oceansoft-lm
1467 csdmbase
1468 csdm
1469 aal-lm
1470 uaiact
1471 csdmbase
1472 csdm
1473 openmath
1474 telefinder
1475 taligent-lm
1476 clvm-cfg
1477 ms-sna-server
1478 ms-sna-base
1479 dberegister
1480 pacerforum
1481 airs
1482 miteksys-lm
1483 afs
1484 confluent
1485 lansource
1486 nms_topo_serv
1487 localinfosrvr
1488 docstor
1489 dmdocbroker
1490 insitu-conf
1491 anynetgateway
1492 stone-design-1
1493 netmap_lm
1494 ica
1495 cvc
1496 liberty-lm
1497 rfx-lm
1498 watcom-sql
1499 fhc
1500 vlsi-lm
1501 saiscm
1502 shivadiscovery
1503 imtc-mcs
1504 evb-elm
1505 funkproxy
1506 utcd
1507 symplex
1508 diagmond
1509 robcad-lm
1510 mvx-lm
1511 3l-l1
1512 wins
1513 fujitsu-dtc
1514 fujitsu-dtcns
1515 ifor-protocol
1516 vpad
1517 vpac
1518 vpvd
1519 vpvc
1520 atm-zip-office
1521 ncube-lm
1522 ricardo-lm
1523 cichild-lm
1524 ingreslock
1525 orasrv
1526 pdap-np
1527 tlisrv
1528 mciautoreg
1529 coauthor
1530 rap-service
1531 rap-listen
1532 miroconnect
1533 virtual-places
1534 micromuse-lm
1535 ampr-info
1536 ampr-inter
1537 sdsc-lm
1538 3ds-lm
1539 intellistor-lm
1540 rds
1541 rds2
1542 gridgen-elmd
1543 simba-cs
1544 aspeclmd
1545 vistium-share
1546 abbaccuray
1547 laplink
1548 axon-lm
1549 shivahose
1550 3m-image-lm
1551 hecmtl-db
1552 pciarray
1553 sna-cs
1554 caci-lm
1555 livelan
1556 ashwin
1557 arbortext-lm
1558 xingmpeg
1559 web2host
1560 asci-val
1561 facilityview
1562 pconnectmgr
1563 cadabra-lm
1564 pay-per-view
1565 winddlb
1566 corelvideo
1567 jlicelmd
1568 tsspmap
1569 ets
1570 orbixd
1571 rdb-dbs-disp
1572 chip-lm
1573 itscomm-ns
1574 mvel-lm
1575 oraclenames
1576 moldflow-lm
1577 hypercube-lm
1578 jacobus-lm
1579 ioc-sea-lm
1580 tn-tl-r1
1581 vmf-msg-port
1582 msims
1583 simbaexpress
1584 tn-tl-fd2
1585 intv
1586 ibm-abtact
1587 pra_elmd
1588 triquest-lm
1589 vqp
1590 gemini-lm
1591 ncpm-pm
1592 commonspace
1593 mainsoft-lm
1594 sixtrak
1595 radio
1596 radio-sm
1597 orbplus-iiop
1598 picknfs
1599 simbaservices
1600 issd
1601 aas
1602 inspect
1603 picodbc
1604 icabrowser
1605 slp
1606 slm-api
1607 stt
1608 smart-lm
1609 isysg-lm
1610 taurus-wh
1611 ill
1612 netbill-trans
1613 netbill-keyrep
1614 netbill-cred
1615 netbill-auth
1616 netbill-prod
1617 nimrod-agent
1618 skytelnet
1619 xs-openstorage
1620 faxportwinport
1621 softdataphone
1622 ontime
1623 jaleosnd
1624 udp-sr-port
1625 svs-omagent
1636 cncp
1637 cnap
1638 cnip
1639 cert-initiator
1640 cert-responder
1641 invision
1642 isis-am
1643 isis-ambc
1644 saiseh
1645 datametrics
1646 sa-msg-port
1647 rsap
1648 concurrent-lm
1649 inspect
1650 nkd
1651 shiva_confsrvr
1652 xnmp
1653 alphatech-lm
1654 stargatealerts
1655 dec-mbadmin
1656 dec-mbadmin-h
1657 fujitsu-mmpdc
1658 sixnetudr
1659 sg-lm
1660 skip-mc-gikreq
1661 netview-aix-1
1662 netview-aix-2
1663 netview-aix-3
1664 netview-aix-4
1665 netview-aix-5
1666 netview-aix-6
1667 netview-aix-7
1668 netview-aix-8
1669 netview-aix-9
1670 netview-aix-10
1671 netview-aix-11
1672 netview-aix-12
1673 proshare-mc-1
1674 proshare-mc-2
1675 pdp
1676 netcomm1
1677 groupwise
1678 prolink
1679 darcorp-lm
1680 microcom-sbp
1681 sd-elmd
1682 lanyon-lantern
1683 ncpm-hip
1684 snaresecure
1685 n2nremote
1686 cvmon
1687 nsjtp-ctrl
1688 nsjtp-data
1689 firefox
1690 ng-umds
1691 empire-empuma
1692 sstsys-lm
1693 rrirtr
1694 rrimwm
1695 rrilwm
1696 rrifmm
1697 rrisat
1698 rsvp-encap-1
1699 rsvp-encap-2
1700 mps-raft
1701 l2f
1702 deskshare
1703 hb-engine
1704 bcs-broker
1705 slingshot
1706 jetform
1707 vdmplay
1708 gat-lmd
1709 centra
1710 impera
1711 pptconference
1712 registrar
1713 conferencetalk
1714 sesi-lm
1715 houdini-lm
1716 xmsg
1717 fj-hdnet
1718 h323gatedisc
1719 h323gatestat
1720 h323hostcall
1721 caicci
1722 hks-lm
1723 pptp
1724 csbphonemaster
1725 iden-ralp
1726 iberiagames
1727 winddx
1728 telindus
1729 citynl
1730 roketz
1731 msiccp
1732 proxim
1733 sipat
1734 cambertx-lm
1735 privatechat
1736 street-stream
1737 ultimad
1738 gamegen1
1739 webaccess
1740 encore
1741 cisco-net-mgmt
1742 3Com-nsd
1743 cinegrfx-lm
1744 ncpm-ft
1745 remote-winsock
1746 ftrapid-1
1747 ftrapid-2
1748 oracle-em1
1749 aspen-services
1750 sslp
1751 swiftnet
1752 lofr-lm
1753 translogic-lm
1754 oracle-em2
1755 ms-streaming
1756 capfast-lmd
1757 cnhrp
1758 tftp-mcast
1759 spss-lm
1760 www-ldap-gw
1761 cft-0
1762 cft-1
1763 cft-2
1764 cft-3
1765 cft-4
1766 cft-5
1767 cft-6
1768 cft-7
1769 bmc-net-adm
1770 bmc-net-svc
1771 vaultbase
1772 essweb-gw
1773 kmscontrol
1774 global-dtserv
1776 femis
1777 powerguardian
1778 prodigy-internet
1779 pharmasoft
1780 dpkeyserv
1781 answersoft-lm
1782 hp-hcip
1783 fjris
1784 finle-lm
1785 windlm
1786 funk-logger
1787 funk-license
1788 psmond
1789 hello
1790 nmsp
1791 ea1
1792 ibm-dt-2
1793 rsc-robot
1794 cera-bcm
1795 dpi-proxy
1796 vocaltec-admin
1797 uma
1798 etp
1799 netrisk
1800 ansys-lm
1801 msmq
1802 concomp1
1803 hp-hcip-gwy
1804 enl
1805 enl-name
1806 musiconline
1807 fhsp
1808 oracle-vp2
1809 oracle-vp1
1810 jerand-lm
1811 scientia-sdb
1812 radius
1813 radius-acct
1814 tdp-suite
1815 mmpft
1818 etftp
1819 plato-lm
1820 mcagent
1821 donnyworld
1822 es-elmd
1823 unisys-lm
1824 metrics-pas
1901 fjicl-tep-a
1902 fjicl-tep-b
1903 linkname
1904 fjicl-tep-c
1905 sugp
1906 tpmd
1907 intrastar
1908 dawn
1909 global-wlink
1911 mtp
1913 armadp
1914 elm-momentum
1915 facelink
1916 persoft
1917 noagent
1918 can-nds
1919 can-dch
1920 can-ferret
1944 close-combat
1945 dialogic-elmd
1946 tekpls
1947 hlserver
1948 eye2eye
1949 ismaeasdaqlive
1950 ismaeasdaqtest
1951 bcs-lmserver
1973 dlsrap
1985 foliocorp
1986 licensedaemon
1987 tr-rsrb-p1
1988 tr-rsrb-p2
1989 tr-rsrb-p3
1990 stun-p1
1991 stun-p2
1992 stun-p3
1993 snmp-tcp-port
1994 stun-port
1995 perf-port
1996 tr-rsrb-port
1997 gdp-port
1998 x25-svc-port
1999 tcp-id-port
2000 callbook
2001 dc
2002 globe
2004 mailbox
2005 berknet
2006 invokator
2007 dectalk
2008 conf
2009 news
2010 search
2011 raid-cc
2012 ttyinfo
2013 raid-am
2014 troff
2015 cypress
2016 bootserver
2017 cypress-stat
2018 terminaldb
2019 whosockami
2020 xinupageserver
2021 servexec
2022 down
2023 xinuexpansion3
2024 xinuexpansion4
2025 ellpack
2026 scrabble
2027 shadowserver
2028 submitserver
2030 device2
2032 blackboard
2033 glogger
2034 scoremgr
2035 imsldoc
2038 objectmanager
2040 lam
2041 interbase
2042 isis
2043 isis-bcast
2044 rimsl
2045 cdfunc
2046 sdfunc
2047 dls
2048 dls-monitor
2049 shilp
2065 dlsrpn
2067 dlswpn
2102 zephyr-srv
2103 zephyr-clt
2104 zephyr-hm
2105 minipay
2201 ats
2202 imtc-map
2213 kali
2221 unreg-ab1
2222 unreg-ab2
2223 inreg-ab3
2232 ivs-video
2233 infocrypt
2234 directplay
2235 sercomm-wlink
2236 nani
2237 optech-port1-lm
2238 aviva-sna
2239 imagequery
2241 ivsd
2279 xmquery
2280 lnvpoller
2281 lnvconsole
2282 lnvalarm
2283 lnvstatus
2284 lnvmaps
2285 lnvmailmon
2286 nas-metering
2287 dna
2288 netml
2307 pehelp
2401 cvspserver
2500 rtsserv
2501 rtsclient
2564 hp-3000-telnet
2592 netrek
2700 tqdata
2784 www-dev
2785 aic-np
2786 aic-oncrpc
2787 piccolo
2788 fryeserv
2789 media-agent
2908 mao
2909 funk-dialout
2910 tdaccess
2911 blockade
2912 epicon
3000 hbci
3001 redwood-broker
3002 exlm-agent
3010 gw
3011 trusted-web
3047 hlserver
3048 pctrader
3049 NSWS
3141 vmodem
3142 rdc-wh-eos
3143 seaview
3144 tarantella
3145 csi-lfap
3264 ccmail
3333 dec-notes
3421 bmap
3454 mira
3455 prsvp
3456 vat
3457 vat-control
3900 udt_os
3984 mapper-nodemgr
3985 mapper-mapethd
3986 mapper-ws_ethd
4000 Remote-Anything
4008 netcheque
4009 chimera-hwm
4132 nuts_dem
4133 nuts_bootp
4134 nifty-hmi
4321 rwhois
4343 unicall
4444 krb524
4445 upnotifyp
4446 n1-fwp
4447 n1-rmgmt
4448 asc-slmd
4449 arcryptoip
4450 camp
4451 ctisystemmsg
4452 ctiprogramload
4453 nssalertmgr
4454 nssagentmgr
4500 sae-urn
4501 urn-x-cdchoice
4672 rfa
5000 commplex-main
5001 commplex-link
5002 rfe
5003 claris-fmpro
5004 avt-profile-1
5005 avt-profile-2
5010 telelpathstart
5011 telelpathattack
5020 zenginkyo-1
5021 zenginkyo-2
5050 mmcc
5145 rmonitor_secure
5150 atmp
5190 aol
5191 aol-1
5192 aol-2
5193 aol-3
5236 padl2sim
5300 hacl-hb
5301 hacl-gs
5302 hacl-cfg
5303 hacl-probe
5304 hacl-local
5305 hacl-test
5400 excerpt
5401 excerpts
5555 personal-agent
5631 pcanywheredata
5632 pcanywherestat
5678 rrac
5679 dccm
5713 proshareaudio
5714 prosharevideo
5715 prosharedata
5716 prosharerequest
5717 prosharenotify
5729 openmail
5745 fcopy-server
5755 openmailg
5757 x500ms
5766 openmailns
5767 s-openmail
5800 VNC
5900 VNC
6000 x11
6110 softcm
6111 spc
6112 dtspcd
6123 backup-express
6141 meta-corp
6142 aspentec-lm
6143 watershed-lm
6144 statsci1-lm
6145 statsci2-lm
6146 lonewolf-lm
6147 montage-lm
6148 ricardo-lm
6149 tal-pod
6253 crip
6389 clariion-evr01
6455 skip-cert-recv
6456 skip-cert-send
6558 xdsxdm
6670 vocaltec-gold
6672 vision_server
6673 vision_elmd
6831 ambit-lm
6969 acmsoda
7000 afs3-fileserver
7001 afs3-callback
7002 afs3-prserver
7003 afs3-vlserver
7004 afs3-kaserver
7005 afs3-volser
7006 afs3-errors
7007 afs3-bos
7008 afs3-update
7009 afs3-rmtsys
7010 ups-onlinet
7099 lazy-ptop
7100 font-service
7121 virprot-lm
7174 clutild
7200 fodms
7201 dlip
7395 winqedit
7491 telops-lmd
7511 pafec-lm
7777 cbt
7781 accu-lmgr
7999 irdmi2
8000 irdmi
8010 wingate-logfile
8032 pro-ed
8080 WWW-Proxy
8450 npmp
8888 ddi-tcp-1
8889 ddi-tcp-2
8890 ddi-tcp-3
8891 ddi-tcp-4
8892 ddi-tcp-5
8893 ddi-tcp-6
8894 ddi-tcp-7
9000 cslistener
9100 JetDirect
9535 man
9876 sd
9992 palace
9993 palace
9994 palace
9995 palace
9996 palace
9997 palace
9998 distinct32
9999 distinct
10000 ndmp
12345 Netbus
12753 tsaf
17007 isode-dua
18000 biimenu
21332 tzo-inet-naming
21845 webphone
21846 netspeak-is
21847 netspeak-cs
21848 netspeak-acd
21849 netspeak-cps
22273 wnn6
22555 vocaltec-wconf
22800 aws-brf
22951 brf-gw
25000 icl-twobase1
25001 icl-twobase2
25002 icl-twobase3
25003 icl-twobase4
25004 icl-twobase5
25005 icl-twobase6
25006 icl-twobase7
25007 icl-twobase8
25008 icl-twobase9
25009 icl-twobase10
25793 vocaltec-hos
25867 WebCam32
26000 quake
26208 wnn6-ds
47557 dbbrowse
47806 ap
47808 bacnet
[ShadowGame World Home] [Game Server IP Address] [Friday Game Info] [LinkSys Help Page] [Search ShadowGameWorld.net]
Copyright © 2001 Shadow Software, Inc.
ShadowSoftware.net is a registered trade mark of Shadow Software, Inc.